Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
湊 太志*; 内藤 智也*; 岩本 修
no journal, ,
Nuclei are excited by muon capture reactions. If the excitation energy is above particle thresholds, the nuclei emit particles competing with the gamma-ray deexcitation. The typical examples are neutron and proton emissions. Other charged particles emissions, like deuteron-,  He-, triton-,
He-, triton-,  -emissions, also occur if the nuclear excitation energy is very high. Information on these particle emissions is important for evaluating soft errors of semi-conductors and radioactivities of materials after irradiations of muon beams. Although experimental data of the particle emissions following muon captures have been reproduced with some phenomenological models, the detailed mechanism with respect to the nuclear structure is still unclear. In particular, experimentally measured neutron spectra after muon capture cannot be reproduced well. We worked on solving this issue with a microscopic approach of second-order proton-neutron Tamm-Dancoff-approximation and particle evaporation models considering pre-equilibrium and compound process. We found that the two-particle two-hole configurations play an important role to reproduce particle spectra obtained after muon captures.
-emissions, also occur if the nuclear excitation energy is very high. Information on these particle emissions is important for evaluating soft errors of semi-conductors and radioactivities of materials after irradiations of muon beams. Although experimental data of the particle emissions following muon captures have been reproduced with some phenomenological models, the detailed mechanism with respect to the nuclear structure is still unclear. In particular, experimentally measured neutron spectra after muon capture cannot be reproduced well. We worked on solving this issue with a microscopic approach of second-order proton-neutron Tamm-Dancoff-approximation and particle evaporation models considering pre-equilibrium and compound process. We found that the two-particle two-hole configurations play an important role to reproduce particle spectra obtained after muon captures.
藤井 大輔; 岩中 章紘*; 保坂 淳*
no journal, ,
基底状態がフレーバー対称性に支配するために、QCD真空の素励起である核子のさらなる性質解明には、その共鳴状態を調べることが有効である。本研究では、ホログラフィックQCDのトップダウンアプローチである酒井杉本模型を用いて、核子共鳴の動的性質、特に電磁遷移振幅や強い相互作用による崩壊過程を調べた。さらに近年注目を集めている、重力形状因子とそこから得られる応力分布に関しても同様の手法により調べた。その結果、応力分布に対する安定性条件とグルーボールのスペクトラの興味深い関係を発見した。
鈴木 渓; 藤井 大輔; 中山 勝政*
no journal, ,
通常のカシミール効果は真空中の光子場に対して定義される物理現象であるが、一方で固体物理で扱われる様々な準粒子場に対してもカシミール効果に相当する新奇な物理現象が生じることがある。原子核物理やQCDの分野においても、高密度クォーク物質/核物質を考えることで、同様の物理現象が実現される可能性がある。例えば、dual chiral density wave (DCDW)相と呼ばれる物質相は、高密度QCDの基底状態の候補として長年研究されている。本講演では、DCDW相におけるクォーク場から生じるカシミール効果の典型的な性質を理論的に示し、カシミールエネルギーなどの物理量が系のサイズの関数として振動する現象を提案する。この現象は、固体物理における対応物であるワイル半金属においても現れることが期待されており、クォーク物質と固体物性系との比較について議論を行う。
廣瀬 健太郎; 西尾 勝久; 牧井 宏之; Orlandi, R.; 塚田 和明; 浅井 雅人; 佐藤 哲也; 伊藤 由太; 洲嵜 ふみ; 田中 翔也*; et al.
no journal, ,
At the JAEA Tokai tandem accelerator facility, we have been studying fission mechanism using multi-nucleon transfer reactions (MNT) through fission observables such as fission-fragment mass distributions, fission probabilities, prompt-fission neutrons, and so on. The MNT reaction is also expected one of viable reactions to produce super-heavy nuclei with more neutrons. The angular momentum transferred in the MNT reaction is an important property since it influences a survival probability of a compound nucleus. In the present study, the angular momentum transferred in MNT reactions are experimentally deduced using fission. In MNT reactions, the axis of the angular-momentum transfer can be defined as perpendicular to the reaction plane. The fission-fragment angular distribution measured with respect to this axis, thus, strongly reflects the angular momentum. We performed measurements of the fission-fragment angular distribution, and deduced the angular momenta transferred to the produced compound nuclei. In this workshop, details of the experiment and results will be presented as well as other experimental activities.
 -ray spectroscopy of heavy actinides at the JAEA Tandem accelerator
-ray spectroscopy of heavy actinides at the JAEA Tandem acceleratorOrlandi, R.
no journal, ,
In the search for superheavy elements, neutron-rich actinides located near proton number Z=100 and neutron number N=152 play a key role to improve our understanding of heavy nuclei and improve current predictions for the location of the island of stability. At the JAEA Tandem accelerator, several actinides in this heavy region of the nuclear chart were studied using  -ray spectroscopy. Isotopes were either excited using Coulomb excitation induced by a
-ray spectroscopy. Isotopes were either excited using Coulomb excitation induced by a  Ni beam (
Ni beam ( Cf,
Cf,  Es), or produced via multi-nucleon transfer reactions of a
Es), or produced via multi-nucleon transfer reactions of a  O beam irradiating a radioactive
O beam irradiating a radioactive  Cf target (
Cf target ( Cf,
Cf,  Fm). In these experiments, the level schemes of these isotopes were significantly extended. In this talk the structure of
Fm). In these experiments, the level schemes of these isotopes were significantly extended. In this talk the structure of  Cf and
Cf and  Fm will be discussed in detail. For the former isotope, delayed transitions observed for the first time reveal the presence of low-lying long-lived states. A
Fm will be discussed in detail. For the former isotope, delayed transitions observed for the first time reveal the presence of low-lying long-lived states. A  isomer with
isomer with 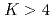 was found at the low excitation energy of approximately 0.9 MeV. This isomer is particularly important to understand the proton orbits near Z=100. In the case of
was found at the low excitation energy of approximately 0.9 MeV. This isomer is particularly important to understand the proton orbits near Z=100. In the case of  Fm, preliminary results will be shown, revealing that
Fm, preliminary results will be shown, revealing that  Fm exhibits the largest moment of inertia among all Fm isotopes, consistent with the largest deformation predicted to occur at the deformed shell gaps (Z=100 and N=152).
Fm exhibits the largest moment of inertia among all Fm isotopes, consistent with the largest deformation predicted to occur at the deformed shell gaps (Z=100 and N=152).
岩本 修
no journal, ,
The latest version of Japanese evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5 was released at the end of 2021. In addition to update of the neutron data in the previous version JENDL-4.0, the upper limit of the incident neutron energy more than 70% of the nuclides in neutron sublibrary was extended to 200 MeV. In addition, the total number of nuclides increased to 795 from the previous number of 406, where activation related data i.e., isomer production information were integrated. JENDL-5 also integrated the various types of reaction data such as photon, proton, deuteron, and alpha-particle induced ones which had been released as special-purpose files of JENDL. Their data were partly updated and complemented to satisfy requirements of radiation transport calculations from the original releases. For the next release of JENDL-5, we are planning to enhance covariance data for neutron reactions whose updates are very limited in JENDL-5. The charged particles reactions, whose data in JENDL-5 are much less than neutron ones, would be also a target of the next release.
浅井 雅人
no journal, ,
 Fm,
Fm,  Fm,
Fm,  Md,
Md,  Lrの自発核分裂に伴う核分裂片の質量分布および全運動エネルギー分布(TKE)を精密に測定した。これらの原子核は、原子力機構タンデム加速器施設において、
Lrの自発核分裂に伴う核分裂片の質量分布および全運動エネルギー分布(TKE)を精密に測定した。これらの原子核は、原子力機構タンデム加速器施設において、 Oビームと
Oビームと Es標的を用いた多核子移行反応及び重イオン核融合-粒子蒸発反応
Es標的を用いた多核子移行反応及び重イオン核融合-粒子蒸発反応 Cm(
Cm( N,4n)
N,4n) Lrにより合成した。核反応生成物はオンライン同位体分離装置ISOLを用いて質量分離し、4組のシリコン半導体検出器を用いて2つの核分裂片の運動エネルギーを同時計数測定した。実験の結果、この中性子過剰フェルミウム核領域では、TKEの高い対称核分裂、TKEの低い対称核分裂、非対称核分裂の3つのタイプの核分裂が競合又は混在することを明らかにした。
Lrにより合成した。核反応生成物はオンライン同位体分離装置ISOLを用いて質量分離し、4組のシリコン半導体検出器を用いて2つの核分裂片の運動エネルギーを同時計数測定した。実験の結果、この中性子過剰フェルミウム核領域では、TKEの高い対称核分裂、TKEの低い対称核分裂、非対称核分裂の3つのタイプの核分裂が競合又は混在することを明らかにした。
佐甲 博之
no journal, ,
本発表ではJ-PARCの将来計画であるJ-PARC重イオン計画(J-PARC-HI)の物理目標、重イオン加速器の計画、実験装置の設計に関して報告する。J-PARC-HIでは世界最高強度の重イオンビームを核子当たり10GeVに加速し、重イオン衝突実験において通常原子核密度の7倍程度の高密度の物質を生成する。本計画は、その物質のレプトン対、事象毎ゆらぎ、フロー、2粒子運動量相関等を測定し、QCD相構造の探索、高密度物質の状態方程式等の性質の研究、あらたな多ストレンジクォークを含むハドロン及び原子核を探索する。
谷田 聖
no journal, ,
Near-threshold molecular-like state may appear as threshold cusp especially when the interaction is not strong enough so that a virtual state is formed instead of a bound state. In this talk, I report on experimental identification of a threshold cusp at Belle and some other related results. I also discuss future plans and possibilities at Belle II and J-PARC.
伊藤 由太
no journal, ,
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)のアイソトープセパレータ・オンライン(ISOL)施設では、イオントラップ技術を用いた短寿命放射性同位元素(RI)の精密実験が準備されている。これにより、中性子過剰核の質量測定や超重元素のトラップ内気相イオン化学など、原子核物理や化学の新たな研究分野を拡大する可能性がある。このような実験を行うためには、電子ボルト領域のエネルギーを持つ低エネルギーRIビームを効率的かつ迅速に生成する必要がある。本研究では、ISOLから入射した30keVのイオンビームを、入射孔を通して100Paのヘリウムガスセルに輸送するために設計されたウィンドウレスガスセルクーラー&バンチャー(GCCB)を開発した。GCCBはその後、ヘリウム原子とのガス衝突のみによってイオンを減速・熱化し、静電減速の必要性を完全に排除する。熱化されたイオンは、RFカーペット、6極イオンガイド、4極マスセパレータなどの高周波(RF)イオンガイド技術を用いて輸送される。ガスセルの性能と取り出し電荷状態の系統性を調べるために、ルビジウム(Z=37)からアクチニウム(Z=89)までの幅広い元素の安定ビームとRIビームを使用した。その結果、抽出電荷状態は3+まで分布し、原子構造に強く依存することがわかった。この結果は、低エネルギーでの電荷変化断面積を計算することを可能にし、超重元素のような1時間に1粒子以下の生成速度しかない元素の抽出イオンビームの電荷状態分布の予測に役立つと考えられる。また、反応ガスを用いて荷電状態を操作し、単一荷電状態を達成するための予備実験も行っている。これはGCCBに続く実験の効率を最大化することを目的としている。
 -ray spectrum for
-ray spectrum for  U(
U(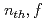 )
)牧井 宏之
no journal, ,
Prompt fission  -ray spectra (PFGS) are important as they allow us to study the structure and de-excitation process of neutron-rich fission fragments (FFs). They are also required as nuclear data to design new types of reactors, such as the Generation-IV reactors. For spontaneous fission of
-ray spectra (PFGS) are important as they allow us to study the structure and de-excitation process of neutron-rich fission fragments (FFs). They are also required as nuclear data to design new types of reactors, such as the Generation-IV reactors. For spontaneous fission of  Cf, the PFGS show broad structures at around
Cf, the PFGS show broad structures at around  -ray energy of 15 MeV, which was explained by incorporating the giant dipole resonance
-ray energy of 15 MeV, which was explained by incorporating the giant dipole resonance  -ray emission. For neutron-induced fissions
-ray emission. For neutron-induced fissions 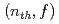 , however, no data are available in the energy range higher than 7 MeV. In this work we extended the measurement of the PFGS for
, however, no data are available in the energy range higher than 7 MeV. In this work we extended the measurement of the PFGS for  U(
U(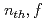 ) up to
) up to 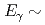 20 MeV by gaining a factor of about 10
20 MeV by gaining a factor of about 10 in statistics compared to the measurements performed so far. The measurement was carried out at the PF1B cold-neutron facility of the ILL, Grenoble, France. The resulting PFGS exhibit local bump structures at
in statistics compared to the measurements performed so far. The measurement was carried out at the PF1B cold-neutron facility of the ILL, Grenoble, France. The resulting PFGS exhibit local bump structures at 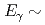 4 MeV and
4 MeV and  6 MeV and also a broad one at
6 MeV and also a broad one at  15 MeV. In this contribution, we will discuss the origins of the bump structures in comparison with the statistical Hauser-Feshbach model calculation.
15 MeV. In this contribution, we will discuss the origins of the bump structures in comparison with the statistical Hauser-Feshbach model calculation.